19 1987 Brief Fact Summary. The Court found that customers have a reasonable expectation of.

Case Closed What Carpenter V United States Means For Your Privacy Bits N Bytes Cybersecurity Education
924 c 1951 a.

Carpenter v us summary. The Supreme Court heard the case on November 29 2017. And others Defendants claiming that the operation of its cattle feedlot constituted. Audio Transcription for Opinion Announcement November 16 1987 in Carpenter v.
Carpenter moved to suppress the governments cell-site evidence on Fourth Amendment grounds arguing that the FBI needed a warrant based on probable cause to obtain the records. The district court denied the motion to suppress and the Sixth Circuit affirmed. Defendants were charged and convicted for violating the mail and.
Carpenter argued that the data collection constituted a search under the Fourth Amendment and required a criminal warrant supported by the higher probable cause standard. This indictment and a bench trial followed. SUPREME COURT OF THE UNITED STATES.
CERTIORARI TO THE UNITED STATES COURT OF APPEALS FOR THE SIXTH CIRCUIT. Prior to trial Carpenter moved to suppress the cell-site data provided by the wireless carriers. The Plaintiffs-Appellants Adrian Carpenter Ruth Carpenter and others Plaintiffs brought suit against the Defendants-Respondents the Double R.
Detroit Timber Lumber Co 200 U. The Fourth Amendment protects the right of people to be secure in their persons houses papers and effects against unreasonable searches and seizures. United States the Supreme Court considered whether the Fourth Amendment permits police to obtain cell phone location records that show an individuals location and movements over the course of 127 days without first obtaining a warrant.
In a majority opinion marked by technological sophistication and powerful arguments about arbitrary government surveillance but overshadowed by four separate dissenting opinions Carpenter both reframes the Fourth Amendment and reveals its fractured soul. Carpenter was charged with six counts of robbery and an additional six counts of carrying a firearm during a federal crime of violence. In a 5-4 decision written by Chief Justice Roberts and invoking the types of government oppression on liberty that led to the American Revolution the Supreme Court reversed the Court of Appeals decision and held that the government must obtain a warrant to search a targets Cell-Site Location Information CSLI.
Because Carpenter involved records acquired from cell phone companies the third-party doctrine was critical to the governments arguments. Although Justice Scalias majority opinion focused on the police placement of the device as a trespass Justices Alito and Sotomayor. In United States v.
United States William H. Cell phones perform their wide and growing variety of functions by con-. After Carpenter was convicted at trial based in part on the cell phone location evidence he appealed to the Sixth Circuit Court of Appeals.
Argued November 29 2017Decided June 22 2018. LEXIS 492 Idaho May 21 1985 Brief Fact Summary. Thereafter the Wall Street Journal and the trade company found out about the agreement.
The opinion of the Court in Number 86-422 Carpenter against United States will be announced by Justice White. As the investigation progressed the conspirators quarreled and on March 29 1984 Winans and Carpenter went to the SEC and revealed the entire scheme. In Carpenter vUnited States Chief Justice John Roberts began the process of future-proofing the Fourth Amendment.
Audio Transcription for Oral Argument October 07 1987 in Carpenter v. Double R Cattle Co 701 P2d 222 108 Idaho 602 1985 Ida. Brant who had pleaded guilty under a plea agreement was a witness for the Government.
Jones the court addressed whether police use of a GPS tracking device required a warrant. Defendants collectively entered in to an agreement which allowed them to take advantage of the stock trade market. Carpenter V United States Ruling Of U S Supreme Court Nwitimes Carpenter V United States 484 U S 19 1987 Case Brief Summary Bee Case Update Carpenter V United States Opinion Ysis Court Holds That Police Will Generally Need A Warrant For Sustained Cellphone Location Information Updated Scotus.

Carpenter V United States American Civil Liberties Union

Justice Gorsuch Carpenter The Fourth Amendment Policybrief Youtube

An Original Fourth Amendment Based On Property Not Privacy By Richard Chen Medium
Case Closed What Carpenter V United States Means For Your Privacy Bits N Bytes Cybersecurity Education
In Carpenter The Supreme Court Rules Narrowly For Privacy The New Yorker
Case Closed What Carpenter V United States Means For Your Privacy Bits N Bytes Cybersecurity Education

Case Closed What Carpenter V United States Means For Your Privacy Bits N Bytes Cybersecurity Education
Case Closed What Carpenter V United States Means For Your Privacy Bits N Bytes Cybersecurity Education

Carpenter V United States Scotusbrief Youtube

Top 10 Privacy Law Developments Of The Decade 2010 2019 Teachprivacy
Case Closed What Carpenter V United States Means For Your Privacy Bits N Bytes Cybersecurity Education

Carpenter V United States Scotusbrief Youtube
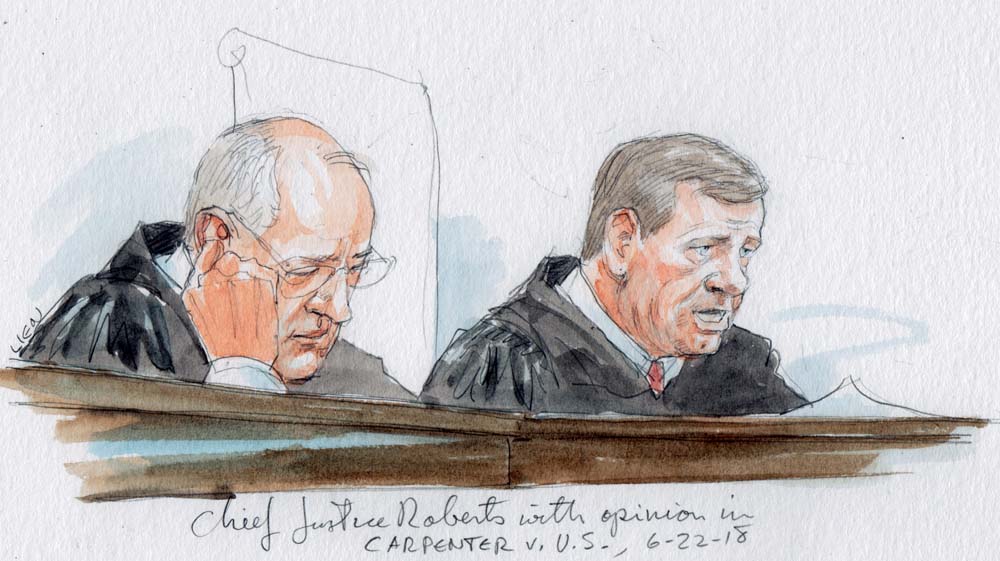

Opinion Analysis Court Holds That Police Will Generally Need A Warrant For Sustained Cellphone Location Information Updated Scotusblog

Image Result For Carpenter V United States The Unit United States Carpenter

Korematsu V United States Case Brief Summary Law Case Explained Youtube
![]()
Top 10 Privacy Law Developments Of The Decade 2010 2019 Teachprivacy

In Carpenter The Supreme Court Rules Narrowly For Privacy The New Yorker

Case Summary Mapp V Ohio 1961 High School Level Street Law Inc
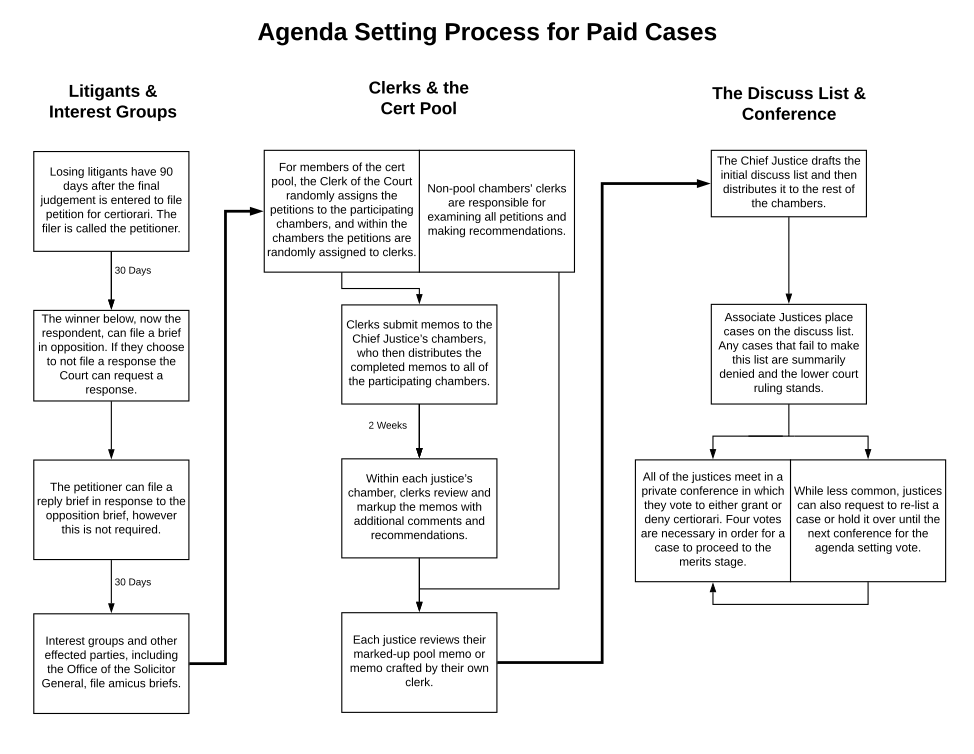
2 3 Judicial Discretion And Us Supreme Court Agenda Setting Open Judicial Politics

